COMPUTER GRAPHICS – “The big space rock will pass close to Earth for Halloween is probably a dead comet, which looks suspiciously like, and timely manner, a skull,” wrote NASA in press
Two dark cavities for eyes, a round hole in the nose dug on a whitish shape shaped skull. photo released by NASA is striking. “The big space rock will pass close to Earth for Halloween is probably a dead comet, which looks strangely and timely manner, a skull,” wrote NASA in a statement released late Friday. “It looks like she has put on a skull costume for his passage (near the Earth) for Halloween,” laughs Kelly Fast, NASA scientist quoted in the release.
The astronomers first thought it was an asteroid when they detected the object early October and they therefore called Asteroid 2015 TB145. But after better observed through infrared telescope NASA (FTIR) based in Hawaii, they “determined that it is most probably a dead comet that lost its volatile materials after many passages around sun, “says the space agency.
Saturday, therefore, on Halloween, a block of several hundred meters in diameter will graze us. Finally, “brush” … This big rock from 200 to 400 meters wide, according to estimates, will increase to 500 000 km from Earth, almost one and half times the distance that separates us from the moon. If this is indeed very close to the scale of the solar system, the risk of collision is perfectly zero. When will pass closer to the Earth, 18 hours, it will also not visible to the naked eye. Not even with binoculars. But since the season is conducive to play to be afraid on this feast of the dead play: could it be that an object of this size hits the Earth one day
The answer is unambiguous?: Yes, it is possible. “It is estimated that the fall of an asteroid than a hundred meters must occur once every ten thousand years, says Patrick Michel, a specialist in asteroids at the Observatoire de Nice Côte d’Azur. An estimate derived from the study of impact craters on the Moon. On Earth, the most recent crater of this category is 60,000 years old. But there is a good chance that other similar-sized asteroids are damaged in the oceans meantime without a trace. “
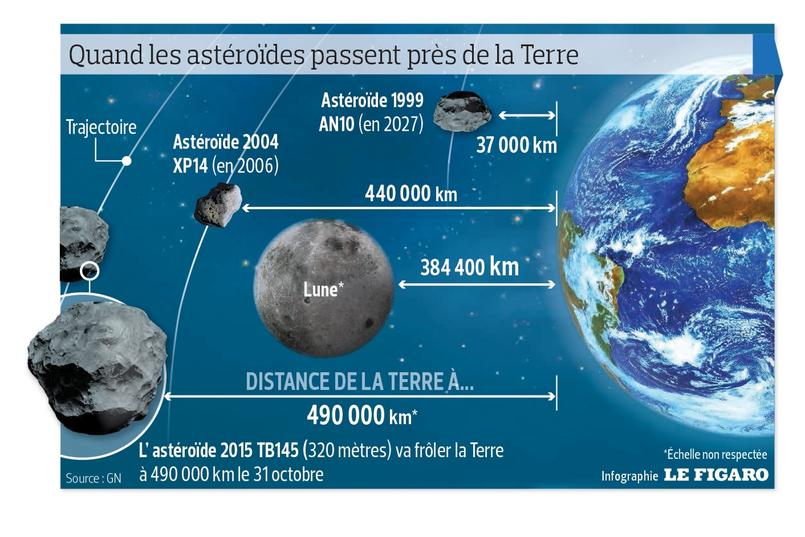
Cliquez for larger computer graphics
That such an object falls on land or at sea, there is a good chance that the consequences are catastrophic. Depending on its speed, density, angle of attack, it could form a crater several kilometers wide and several hundred meters depth, or cause a wave of several hundred meters. The whole surrounding area would be impacted hundreds of kilometers around. The death toll would amount very probably millions or even tens of millions.
As for objects larger than one kilometer in diameter, they would be able to annihilate humanity. Fortunately, they are more rare: it falls that approximately every 500,000 years. Over 90% of them have already been identified and do not present a medium-term threat.
“If we’re seeing dangerous asteroids with a few years’ advance, then it would still be possible to deflect them from their path “
We do not know, however, that 10-15% of asteroids of more than 150 meters in diameter. Our asteroid – or comet – Halloween, appointed in 2015 TB145, for example has been detected last October 10 by the Pan-STARRS telescope Space-1 University of Hawaii. This ignorance is alarming enough that NASA has recently undertaken under the program SpaceGuard (literally “guardian of space”), the census of all these objects. Objective: to identify 90% of them by 2025
It is not excluded that other such objects are discovered yet only weeks before presenting a danger to Earth. . It would be too late for anything. “But if we see them arrive with a few years in advance, then it would still be possible to deflect them from their path,” says Patrick Michel. Aida mission being evaluated by the European and American space agencies, and is considering very seriously to test an impactor to an asteroid in 2022.
It would be better none have the bad idea we cross before then. We would then have no solution that has ever been the slightest test, which could seriously complicate policy discussions. “But the longer it is usually to make a decision,” recalls Patrick Michel philosophy.
Meanwhile, astronomers will enjoy this close fly TB145 2015 to study it closely. It should be possible to obtain radar images with unprecedented definition of two meters per pixel. A real bargain: the next flyover so near such a large object is not expected before 2027. Except last minute surprise, of course
.
No comments:
Post a Comment